As consumer attitudes shift in favor of intelligent, software-powered vehicles, there has been a rapid global commercialization of mobility transportation services developed by mobility platform operators. Several autonomous mobility services have emerged, each with their distinct technological, regulatory, and economic profiles.
Among these services, robotaxi commercialization is proceeding faster than that of other autonomous mobility services due to a convergence of regulatory flexibility, scalable profitability models, and accelerated technological innovation. This momentum is further fueled by growing public expectations that robotaxis will emerge as a mainstream urban mobility solution, offering a cost-effective alternative to both traditional taxis and privately owned vehicles.
At the same time, cybersecurity concerns have surfaced around autonomous robotaxi fleets, as a single vulnerability could potentially impact multiple vehicles and pose serious risks to public safety. This article aims to showcase the current status surrounding robotaxi commercialization and emphasize the importance of maintaining safe cybersecurity measures as robotaxis permeate more into everyday life.
Robotaxi Service Development by Region
Across the robotaxi ecosystem, service development among mobility providers spans multiple stages ranging from trials and pilots to commercial operations and mass deployment. Regional regulatory environments have been playing a critical role in shaping business strategies, with service providers typically expanding globally following proven success in their domestic markets.
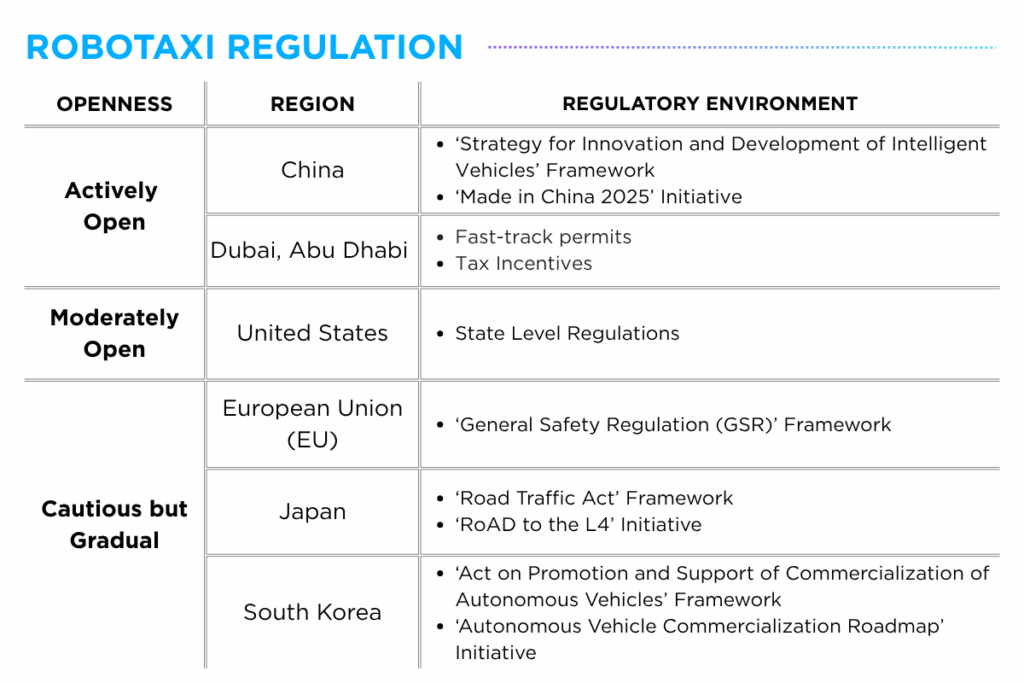
Among the more regulatory-open regions are China, Dubai, Abu Dhabi and the United States, where governments have actively introduced dedicated frameworks and launched national initiatives to support the commercialization of autonomous robotaxis. Companies such as Baidu, Pony.ai and WeRide have expanded their presence in these markets through strategic partnerships with local taxi operators and public agencies.
Meanwhile, countries such as Japan and South Korea have adopted a more measured approach to autonomous driving regulation, with services providers such as Avride, TIER IV and Motional conducting pilot programs in designated areas as they work toward full-scale commercialization.
Global Robotaxi Commercialization Trends
Observing the activities of global robotaxi service providers across key cities, several emerging patterns in commercialization efforts can be derived.
First, major operators are actively expanding into the United Arab Emirates (UAE), signaling the region’s growing openness to autonomous mobility. WeRide and Uber launched their first international robotaxi service in Abu Dhabi in December 2024, and extended their partnership to Dubai in April 2025, with the goal of integrating robotaxis into the city’s transportation network. Baidu has also partnered with UAE-based Autogo, targeting the start of commercial operations in Abu Dhabi by 2026, with pilot trials expected in Dubai within 2025.
Second, the global autonomous vehicle industry is increasingly defined by a two-track development model – China emerging as a leading hub for commercial deployment, and the United States serving as a focal point for research and development. AutoX, headquartered in San Jose, California, launched its Level 4 driverless robotaxi service to the public in Shenzhen, China in 2021. Similarly, Pony.ai operates dual headquarters in the US and China, with large-scale robotaxi fleets running in cities like Beijing and Guangzhou, while pilot programs continue in California cities such as Fremont and Irvine.
Third, US-based companies are steadily expanding robotaxi operations across state lines, navigating a fragmented regulatory landscape in the absence of a unified regulatory framework. As of May 2025, Waymo provides over 250,000 paid driverless rides per week across cities including San Francisco, Los Angeles, Austin, Phoenix and Austin, with plans to enter new markets such as Atlanta, Miami and Washington, D.C. by 2026. Meanwhile, Tesla is preparing to launch its robotaxi service in Austin in June 2025, with expectations that the service expand to additional cities once operational stability is achieved.
Cybersecurity Concerns around Robotaxis
While autonomous robotaxis hold significant promise for improving urban mobility through enhanced convenience and accessibility, cybersecurity risks remain a critical concern. Although no confirmed cases of malicious hacking specifically targeting autonomous robotaxis have been reported to date, incidents involving software malfunctions have nonetheless heightened public unease around the reliability of these systems.
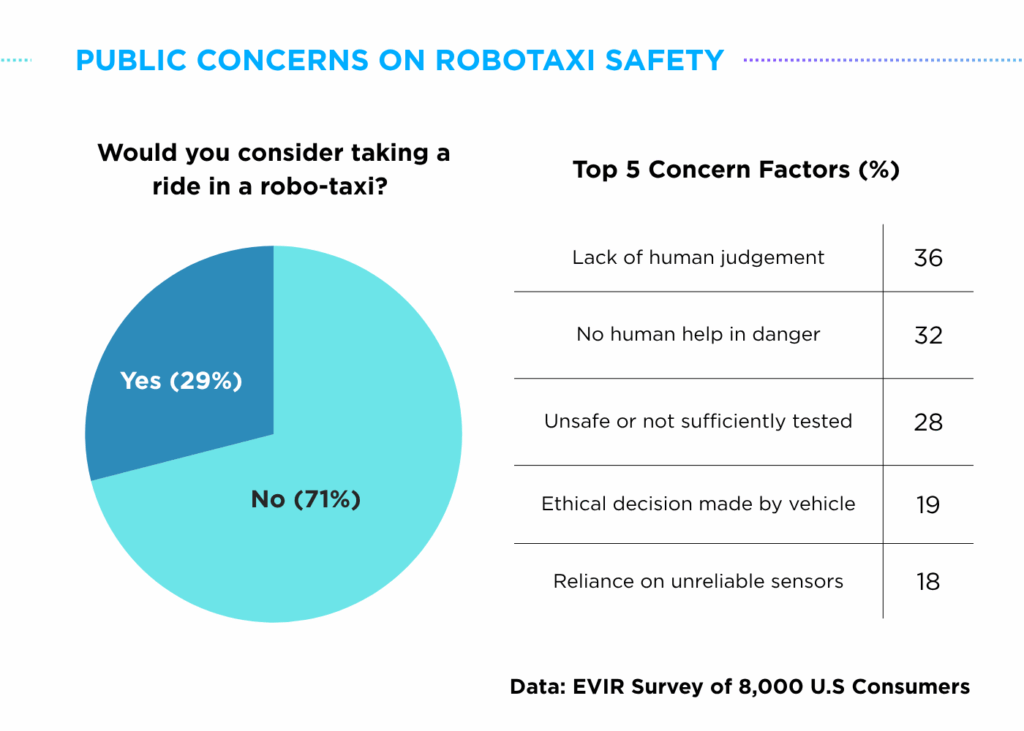
This growing apprehension is reflected in the ‘Electric Vehicle Intelligence Report (EVIR) 2025 May Edition’ where 71% of respondents showed reluctance to riding a robotaxi. Among the key concerns regarding robotaxi rides, 28% of respondents cited safety issues related to robotaxi use, while 18% expressed worry about over-reliance on sensors.
Unlike privately owned autonomous vehicles, cyberthreats to robotaxis carry heavy significance as a vulnerability in one model or system could potentially affect the city-wide transportation systems connected with internal and external data streams. As these services scale, it becomes vital to implement robust, end-to-end cybersecurity measures to ensure the safety of the vehicles, passengers and ultimately the entire mobility ecosystem.
Autocrypt’s Technical Expertise
Through a multi-layered approach that integrates advanced technologies, regulatory compliance, and industry collaboration, Autocrypt is well positioned to address the cybersecurity challenges associated with public mobility services.
With solutions spanning the entire autonomous ecosystem – from securing V2X communication security with AutoCrypt V2X, to safe-guarding in-vehicle security systems through AutoCrypt IVS, and overseeing operational data from AutoCrypt FMS – potential risks around mobility services can be prevented beforehand, enhancing the overall safety of connected mobility environments.
As the rapid advancement of robotaxi services marks a pivotal step toward the integration of autonomous vehicles into mainstream mobility networks, it is critical to raise cybersecurity awareness and implement preventive safeguards. Doing so will be essential to ensuring public trust and unlocking the full potential of autonomous mobility.
To learn more about the latest news on mobility tech and software-defined vehicles, read our blog for more technology insights or subscribe to AUTOCRYPT’s monthly newsletter.

![[AUTOCRYPT] CES 2026 Highlights](https://autocrypt.io/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/12_8-D-30_2-est-2.png)


