Public transportation is undergoing a profound transformation. What was once limited by fixed timetables and rigid infrastructure is evolving into an intelligent, adaptive network powered by real-time data, electrification and automation. Beyond technological progress, this shift reflects a move toward a mobility model driven by cooperation and shared innovation.
Cities, governments, and transport authorities are increasingly co–developing mobility services with private technology providers to address emerging urban and societal needs. Many of these efforts are guided and supported by national and bilateral innovation initiatives, providing the funding and regulatory frameworks needed to connect public governance with private technological capability.

This blog highlights the global trend through initiative-backed examples, showing how collaboration between public entities and private firms is reshaping the future of public transportation.
Rise of Adaptive Public Mobility Ecosystems
Traditional fixed-route transit systems are increasingly challenged by uneven ridership patterns, with dense urban areas often overcrowded while suburban and rural regions remain underserved. To close this gap, cities and transport authorities are adopting digitally integrated, AI-powered systems that can adjust dynamically to real-time demand, ensuring more efficient and inclusive operations.
The following case studies illustrate how initiative-backed partnerships are aligning public governance with private innovation, advancing adaptive, data-driven mobility solutions through the combined expertise of governments and technology leaders.

Case 1: Shucle DRT Pilot (Hungary, 2025)
The Hyundai Shucle pilot in Hungary was launched under the Economic Innovation Partnership Program (EIPP), a Korea-Hungary bilateral cooperation framework led by the Ministry of Economy and Finance (MOEF) and the Korea Development Institute (KDI). Under the initiative’s design on promoting innovation-driven development projects, the pilot aims to introduce an AI-powered Demand-Responsive Transport (DRT) solution which enhances operational efficiency and accessibility within Hungary’s public transit systems.
On the public side, MOEF and KDI oversee funding, policy design and program monitoring, while the Gödöllő Municipality and local transport operators act as pilot hosts, integrating the service into the local transit network. As the private partner, Hyundai Motor Group provides and operates the Shucle platform, which leverages AI for dynamic routing, real-time demand optimization and fleet management.
The project demonstrates how bilateral innovation programs can effectively bridge public governance and private technology to deliver tangible mobility improvements.
Case 2: NoWel4Project (Germany, 2024-2026)
The NoWel4Project originates from Germany’s Federal Ministry for Digital and Transport (BMDV) R&D program for Autonomous and Connected Driving. The initiative focuses on deploying Level 4 autonomous electric shuttles in northwest Berlin to explore how automated mobility can be integrated safely and effectively into existing public transport networks.
BVG, Berlin’s public transport operator, manages route planning, service integration and regulatory compliance, while academic and institutional partners, including TU Berlin and IKEM, contribute to research and policy framework development. The private partner, MOIA GmbH, a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group, provides and operates ID.Buzz AD shuttles equipped with Level 4 automation and oversees software management, connectivity and fleet operations.
Together, the partners represent Germany’s coordinated approach to incorporating advanced automation within the public transport ecosystem.
Case 3: National Diet Shuttle (Japan, 2025)
In a more recent case, TIER IV was selected to lead a public-sector autonomous shuttle project connecting government buildings around Japan’s National Diet in central Tokyo. Funded by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), the initiative aims to accelerate the adoption of autonomous driving technologies within public services, addressing broader social challenges such as an aging populations and driver shortages in municipalities beyond major metropolitan areas.
Powered by Autoware™, the open-source autonomous driving software developed by TIER IV, the system utilizes Suzuki’s Solio model and implements TIER IV’s robotaxi reference design. The service began operations on November 20, 2025, with project findings expected to inform Japan’s future frameworks for autonomous mobility procurement and deployment.
This example illustrates Japan’s commitment to technology-driven public innovation, embedding autonomous mobility into public infrastructure to enhance transportation efficiency while advancing social sustainability.
Case 4: Autonomous Shuttle Pilot (Singapore, 2025)
In Singapore, the partnership between WeRide and Grab operates under the Land Transport Authority (LTA)’s regulatory sandbox for autonomous vehicle testing, part of the nation’s Smart Nation and Land Transport Master Plan. Under a framework that enables real-world testing of autonomous mobility technologies in designated smart zones, the pilot conducts large-scale trials of autonomous shuttles in Singapore’s Punggol district to evaluate service readiness before public launch in early 2026.
Guided by the LTA, which ensures compliance with national safety and operational standards, the pilot brings together two private partners, each contributing distinct technical and operational strengths. WeRide, serving as the technology provider, supplies autonomous driving systems and vehicles while managing fleet operations and safety monitoring. Grab, leveraging its operational and local expertise, handles service deployment, customer interface, and integration with its existing ride-hailing platform.
This initiative stands to illustrate a regulatory-sandbox approach where public oversight and private innovation intersect to validate autonomous mobility services for commercial deployment.
Implications
Despite regional and strategic variations, the four cases trace a clear progression in how adaptive public mobility is evolving through public-private collaboration.
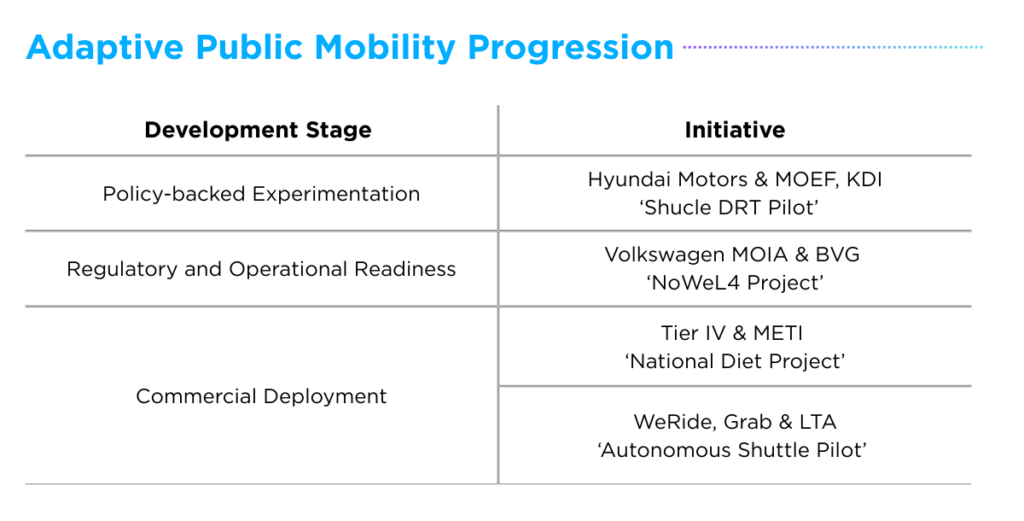
The ‘Shucle DRT Pilot’ demonstrates how bilateral innovation programs can initiate policy-backed experiments that connect governance with technology. Building on this foundation, both the ‘NoWel4 Project’ and ‘National Diet Project’ exemplify how coordinated public initiatives are advancing regulatory and operational readiness for autonomous urban transit. Finally, the ‘Autonomous Shuttle’ pilot highlights the transition from controlled testing to commercial deployment, illustrating how proven technologies can scale into real-world, revenue-generating services.
Together, they pursue the same overarching goal: to enhance accessibility, efficiency and adaptability within public transportation systems and highlight a global shift toward an adaptive mobility framework.
Future of Connected Mobility
As cities worldwide adopt adaptive mobility frameworks, their success increasingly depends on secure, interoperable collaboration between public and private stakeholders. Ensuring seamless communication among vehicles, infrastructure, and digital platforms requires standardized protocols, trusted data exchange and end-to-end cybersecurity. Without these foundations, the integration of connected and autonomous mobility remains incomplete.
AUTOCRYPT plays a defining role in enabling this transformation. In particular, AutoCrypt® MOVE™ (Learn More) is one such solution which shows our capabilities into the mobility platform domain. Designed for demand-responsive transport (DRT) and other emerging mobility services, AutoCrypt® MOVE™ enables operators to plan, deploy and manage secure, data-driven mobility platforms tailored to diverse needs.

By combining our proven expertise in fleet management, data analytics, and security integration, AUTOCRYPT supports both public transit operators and private mobility providers in establishing reliable and adaptive services.
With expertise spanning digital key management, V2X communication, cybersecurity testing and compliance consulting, AUTOCRYPT provides the technologies and guidance that help stakeholders operate securely within complex mobility environments. By embedding safety and interoperability into every layer of mobility infrastructure, AUTOCRYPT helps build a trusted, scalable, future-ready ecosystem which benefits both public and private partnerships.
To learn more about end-to-end mobility solutions, visit https://autocrypt.io/all-products-and-offerings/

![[AUTOCRYPT] CES 2026 Highlights](https://autocrypt.io/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/12_8-D-30_2-est-2.png)


