AUTOCRYPT, award-winning vehicle testing solutions provider, and Hitachi Solutions, Ltd., IT solutions provider, announced a distribution agreement, bringing AutoCrypt Security Fuzzer to the Japanese market starting January 22, 2025. This marks the first domestic availability of the globally recognized Security Fuzzer in Japan.
This adds to the two companies’ existing partnership agreement, as AUTOCRYPT currently offers its V2X security solution with the option of integrating its security library with Hitachi Solution’s Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Middleware Platform. The new agreement continues to align with Hitachi Solutions’ commitment to delivering advanced cybersecurity tools, as well as AUTOCRYPT’s expertise in developing cutting-edge, optimized testing technologies to the automotive industry.
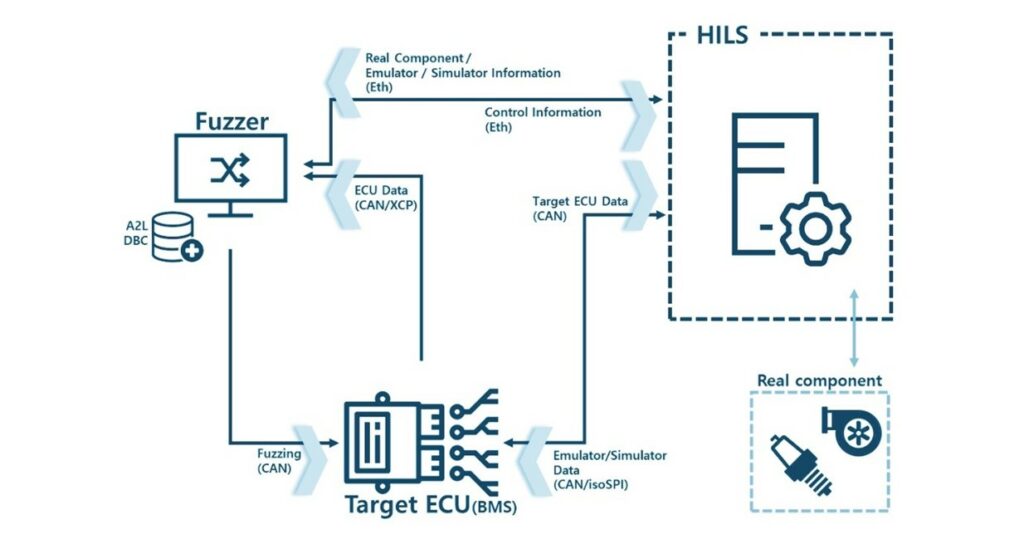
AutoCrypt Security Fuzzer was designed specifically for in-vehicle software development and testing, and boasts automated test case generation, generating over one million test cases based on ISO 14229-1:2020, supporting all 26 Service Identifiers (SIDs) defined in the Unified Diagnostic Service (UDS) protocol). AutoCrypt Security Fuzzer also provides continuous automated execution for individual ECUs or integrated systems, optimizing the testing process. Users receive comprehensive key test results, with summaries and visualizations of major outcomes, enabling developers to quickly review and re-execute to address detected vulnerabilities.
“We are delighted to work together with Hitachi Solutions to bring our fuzzing solution to the Japanese market,” said Duksoo Kim, CEO and co-Founder of AUTOCRYPT. “As the industry embraces SDVs, there is mounting pressure for manufacturers and suppliers to meet standards and regulations, and our tool offers support so there is no interruption in the compliance process. We are confident that AutoCrypt Security Fuzzer will address the current challenges in the automotive cybersecurity landscape, and contribute to safer, more reliable automotive software.”
The official distributorship agreement in Japan through Hitachi Solutions will enable Japanese manufacturers and suppliers to adopt a comprehensive, effective approach to cybersecurity testing, streamlining compliance with international standards, including ISO/SAE 21434.
About Autocrypt Co., Ltd.
AUTOCRYPT is the leading player in automotive cybersecurity and smart mobility technologies. It specializes in the development and integration of security software and solutions for in-vehicle systems, V2X communications, Plug&Charge, and fleet management, paving the way towards a secure and reliable C-ITS ecosystem in the age of software-defined vehicles. Its comprehensive suite of automotive cybersecurity testing services and platforms includes the award-winning AutoCrypt CSTP, which supports automotive OEMs and suppliers in meeting regulatory standards ilke ISO/SAE 21434, UNECE WP.29 UN R155, as well as other emerging global standards.
About Hitachi Solutions, Ltd.
Hitachi Solutions is a core IT company of the Hitachi Group. They deliver products and services of superior value to customers worldwide through key subsidiaries in Asia, the United States and Europe. Hitachi Solutions has also been providing a variety of solutions globally using cutting-edge digital technologies based on collaborative creation with customers. Together with our partners around the world, They are accelerating Sustainability Transformation (SX) to solve the challenges facing society and business, and contribute to the realisation of a happy society where no one is left behind.