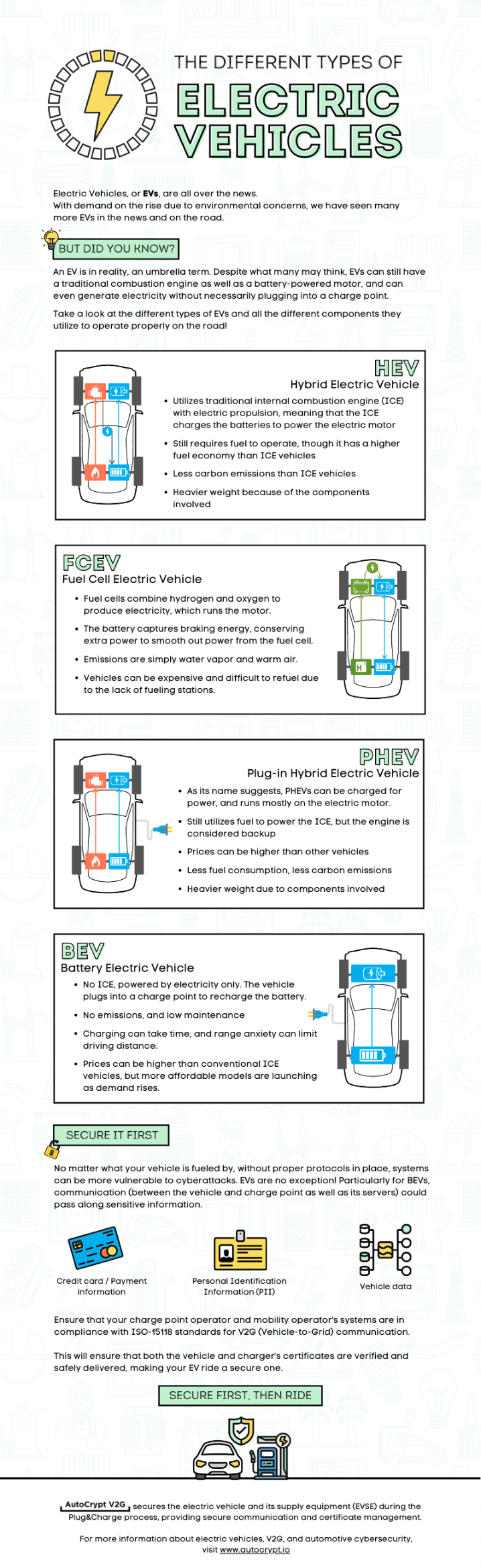
SAN FRANCISCO, July 8, 2024 — Emobi and Autocrypt today announced the first US-based Plug & Charge ecosystem, set to revolutionize electric vehicle (EV) charging with artificial intelligence (AI).
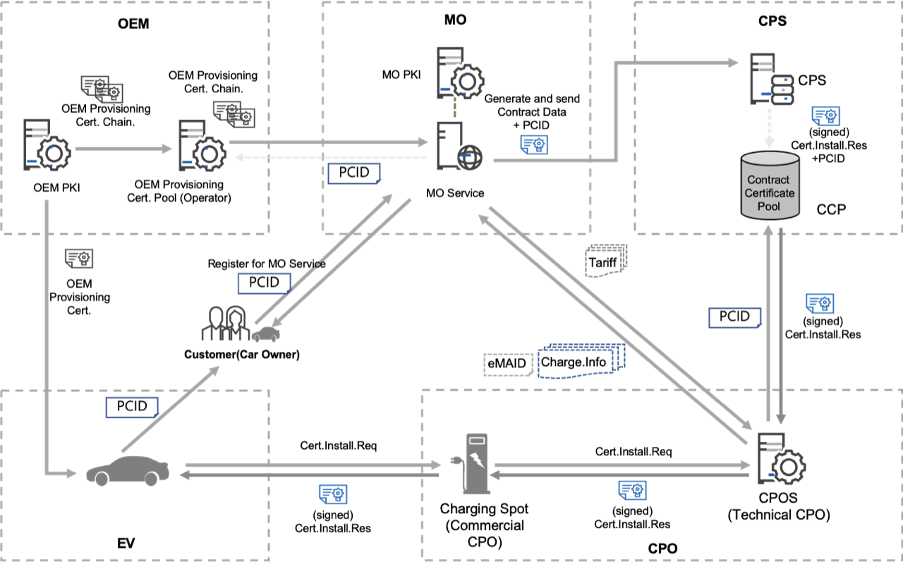
In June 2023, Autocrypt, a global leader in automotive cybersecurity, partnered with Emobi, a US-based e-mobility hub, to develop a secure communication framework for EVs and charging stations based on ISO 15118-2 and ISO 15118-20 standards. The collaboration has focused on building a robust Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) utilizing fine-tuned AI and machine learning models to address errors and data inconsistencies prevalent in traditional Plug & Charge systems.
The Plug & Charge ecosystem enables EV drivers to start charging at any station simply by plugging in their vehicle. Through asymmetric encryption technology, the chargers automatically identify the EV and securely process the payment of the EV charging session. Unlike other Plug & Charge services, this is the first Plug & Charge ecosystem headquartered in the United States, ensuring data security and compliance with the US government. Additionally, it features an intelligent error-handling system that addresses edge cases in ISO 15118 standards, setting a new benchmark for the industry.
Throughout this collaboration, Emobi has worked closely with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory to ensure that findings from this ecosystem contribute to the National Charging Experience (ChargeX) Consortium, funded by the Joint Office of Energy and Transportation of the United States.
“Security in EV charging infrastructure enhances openness while providing better control,” said Sean HJ Cho, President of Autocrypt North America. “By combining our PKI technology with Emobi’s expertise in AI and machine learning, we are bringing a secure yet innovative Plug & Charge solution to market, creating an unrestricted charging environment that ensures convenience, precision, and security throughout the entire charging and payment processes.”
Lin Sun Fa, CEO of Emobi, added, “The focus is to enable EV automakers, charger operators, and e-mobility service providers to continue building their products without being hindered by edge cases and constantly evolving standards. We are leveraging AI and Autocrypt’s PKI technology within the existing ISO 15118 standards, ensuring ease of implementation while improving charging infrastructure quality and security.”
About Autocrypt Co., Ltd.
AUTOCRYPT is the industry leader in automotive cybersecurity and connected mobility technologies. The company specializes in the development and integration of security software and solutions for in-vehicle systems, V2X communications, Plug&Charge, and mobility platforms, paving the way towards a secure and reliable C-ITS ecosystem in the age of software-defined vehicles. AUTOCRYPT also provides consulting and testing services along with custom solutions for UN R155/156 and ISO/SAE 21434 compliance.
About Emobi
EMOBI is the EV charging ecosystem that powers hundreds of e-mobility businesses with AI. The ecosystem offers instantaneous access to a vast network of EV charging networks and e-mobility partners, while ensuring superior data quality through its refinement models. With over 120,000 connected charging ports in the United States and Canada, Emobi has established itself as the largest roaming hub in North America powered with AI. In addition, Emobi has garnered trust in the e-mobility market, advising leading EV manufacturers, e-mobility enterprises, startups, utilities, and esteemed U.S. Government Agencies like the Department of Energy (DoE) and the Department of Transportation (DoT).