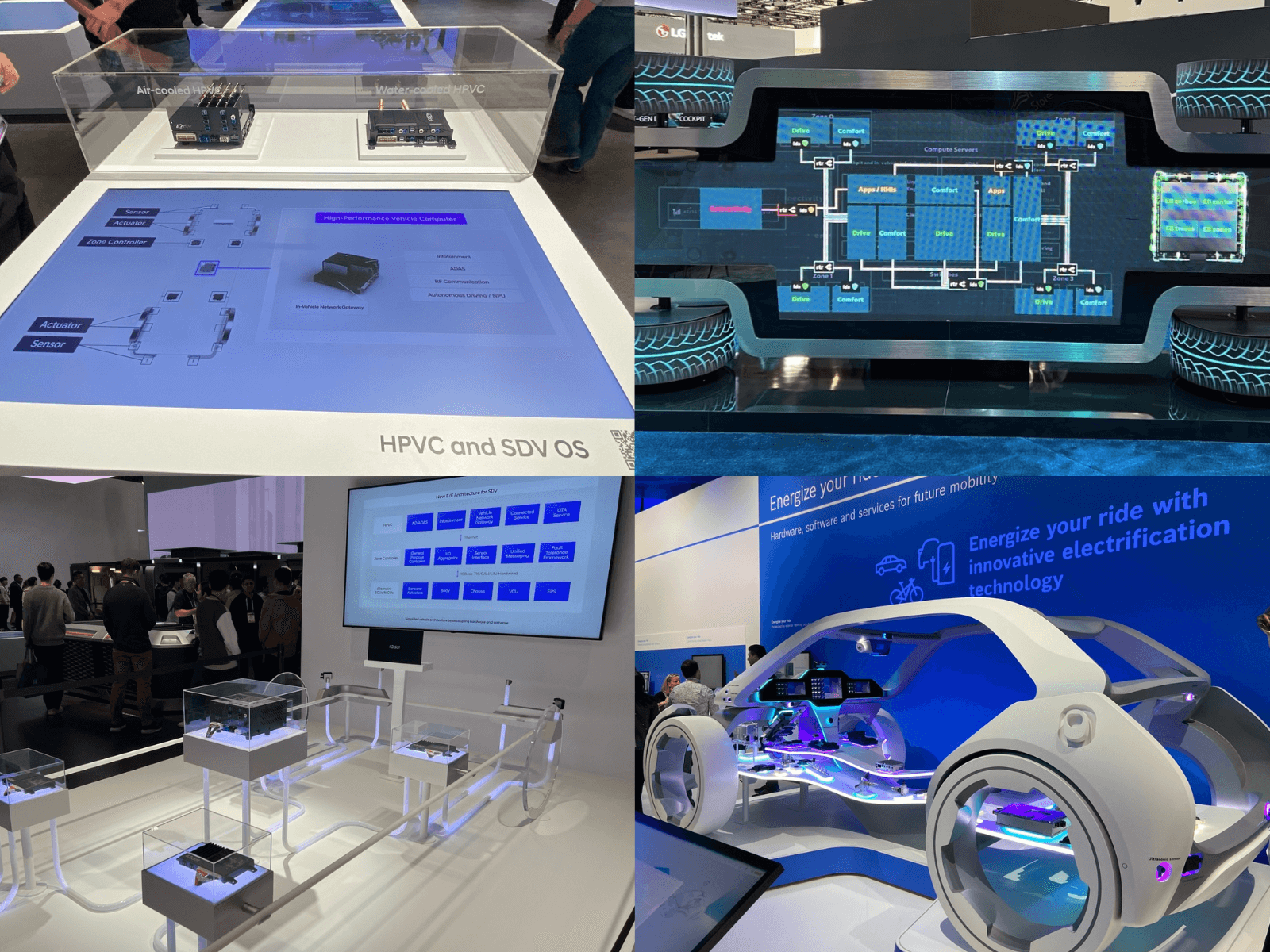
CES 2024 introduced the world to the new era of software-defined vehicles, signifying the beginning of a massive technology transition in the automotive field. At its CES debut, AUTOCRYPT emphasized the importance of automotive cybersecurity for software-defined vehicles, while demonstrating its security solutions and testing tools for in-vehicle systems and V2X communications.
On January 9, 2024, AUTOCRYPT made its first appearance at CES, the world’s most influential tech event. Taking place conveniently at the beginning of the year, CES is the biggest stage for tech companies across the globe to showcase their innovations of the year. This year, more than 4,000 exhibitors and over 130,000 industry attendees gathered in Las Vegas for the show.
Originally known as the Consumer Electronics Show, the scope of CES has expanded far beyond consumer electronic products and now encompasses all types of technologies used throughout all stages of the value chain. Starting in 2019, the automotive tech industry has been playing an increasingly dominant role at the show, showcasing advanced automotive technologies like electric vehicles and autonomous vehicles.
Vehicle Tech Trend at CES 2024: Software-Defined Vehicles
At CES 2024, vehicle and mobility-related technology accounted for nearly half of the entire exhibition. The automotive industry has now become the center of technology innovations, a phenomenon driven by two major transitions in the industry:
- The shift from internal combustion engines to electric motors
- The switch from hardware-centric to software-centric vehicular architecture
The first transition was shown in previous CES exhibitions, where manufacturers showcased their latest electric vehicle models and concepts. The share of electric vehicles on the roads has also increased significantly throughout the past few years. CES 2024 brought the focus to the second transition, which has been less apparent to the public. Automotive OEMs and suppliers are now showcasing the latest software-centric architecture, operating systems, platforms, and applications, all of which are based on the fundamental concept of software-defined vehicles.
Breaking Down the Software-Defined Vehicle
What is the SDV?
The term “software-defined vehicle”, or “SDV”, has been widely used within the automotive industry to describe cars whose functionality and features can be upgraded over time through software updates. These cars provide a user experience comparable to smartphones and computers, often equipped with a tablet-like central console that controls all features.
Standardized middleware
The transition to SDVs requires a complete overhaul of the automotive manufacturing process. The transition not only requires the decoupling of hardware and software, but also the ability to perform software updates to specific components without impacting the interoperability of these components with the rest of the vehicle. The AUTOSAR Adaptive Platform is a middleware built for this purpose, allowing different manufacturers to build and update software on a standardized platform. In the end, automotive OEMs will need to dedicate most of their resources to software consolidation rather than hardware assembly.
Growing range of communication protocols
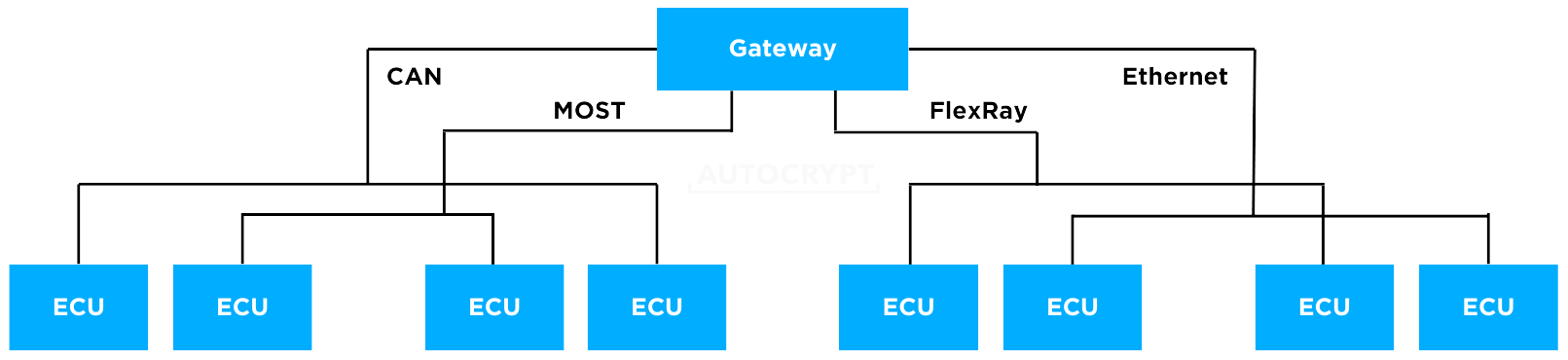
The growing diversity of vehicular applications leads to a growing need for dedicated communication protocols. The fundamental CAN (CAN FD) and FlexRay buses are signal-based communication channels necessary for real-time safety-critical (ASIL-D) use cases, such as braking, steering, airbag activation, and engine control. Yet, these protocols do not carry enough bandwidth for multi-tasking and large-size data transfer. This led to the implementation of many new communication protocols. Ethernet, for instance, is becoming increasingly prevalent in cars as it offers extremely high bandwidth at a cheap cost, best suited for advanced applications. SOME/IP is used to connect ECUs with different sizes, such as the in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), head unit, telematics control unit, and cameras.
Centralized E/E architecture
With the growing number of advanced features, a high-end car can have up to 300 ECUs. This is overly complex to build on a conventional distributed E/E architecture—there is simply not enough room to fit all the cables and wires.
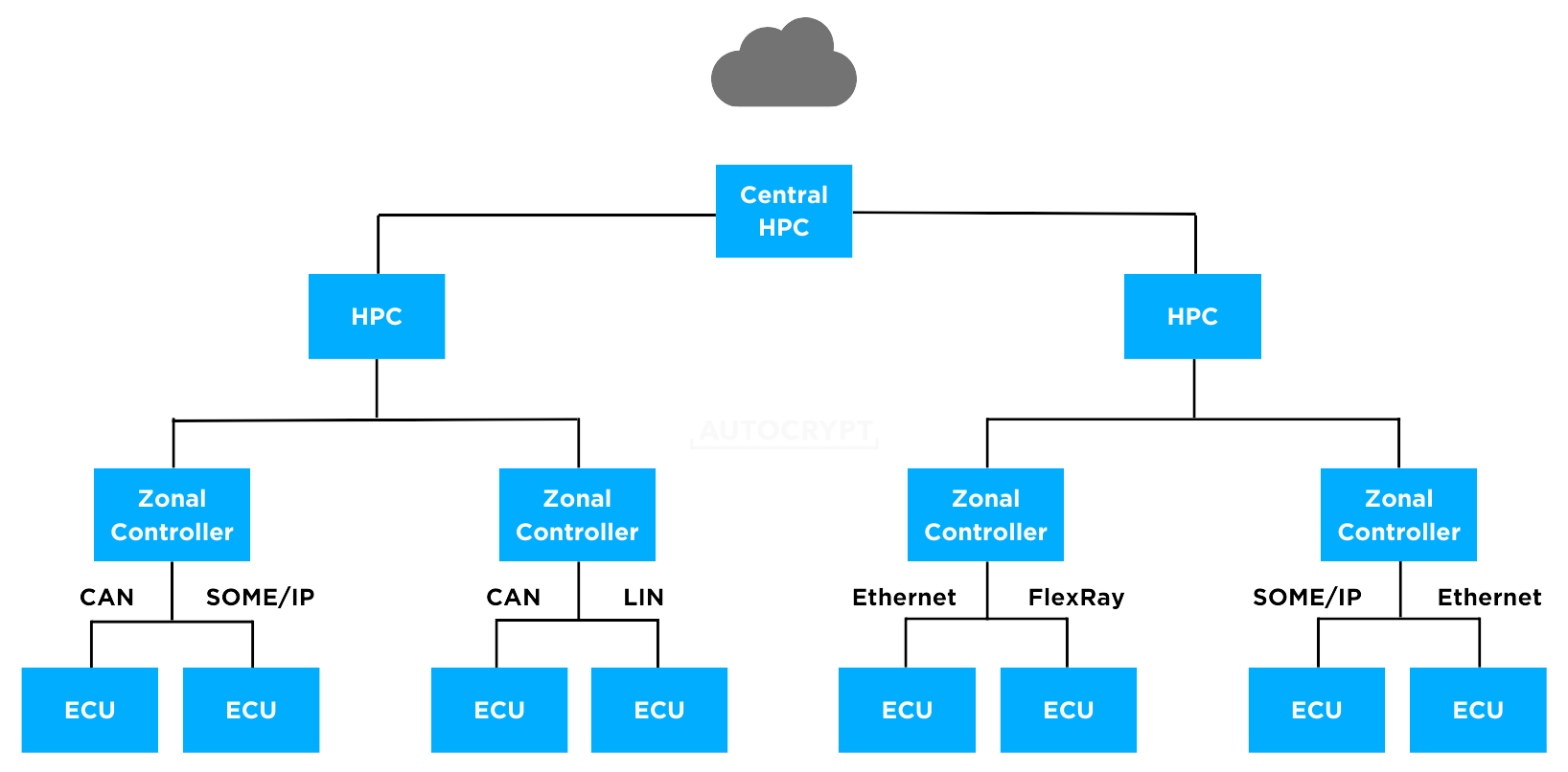
To reduce the number of cables and wires while accommodating all the advanced applications, advanced processors like zonal controllers and high-performance computers (HPC) must be adopted. Different from controller-based ECUs, these processor-based ECUs consolidate a wide range of software from different domains and process them on a single central computing unit. Since they can communicate via multiple protocols, functional domains like ADAS, IVI, and body control can all be executed on a single HPC.

Automotive OS
The complete software stack of a software-defined vehicle is commonly referred to as the “automotive OS”. This contains the HPC, the hypervisor—which allows the HPC hardware to execute both backend applications and the frontend UX, the backend OS (OSEK OS, Linux, QNX), the user OS (Android Automotive – not to be confused with Android Auto), the AUTOSAR Adaptive stack, and the applications—often placed in containers for easy management and update.
Automotive cybersecurity
As automotive OEMs become software companies, cybersecurity becomes essential. In fact, cybersecurity is an integral component of SDVs, as standardized by ISO/SAE 21434 and regulated by UN Regulations 155/156. When implementing the automotive OS, end-to-end encryption, two-way authentication, and threat detection mechanisms must be incorporated to secure the in-vehicle network and monitor abnormal ECU activities.
Besides embedded security software, automotive cybersecurity must begin at the vehicle development stage, where vulnerability tests like software composition analysis and fuzzing have become legal requirements.
As an industry-leading automotive cybersecurity company, AUTOCRYPT offers a comprehensive cybersecurity solution for software-defined vehicles, covering vulnerability testing, TARA, and embedded security, all of which are custom-built to support all types of communication protocols and platforms. Its latest development – AutoCrypt Security Fuzzer for HIL – enables fuzz testing in hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation environment.
The Future of SDVs: Autonomous Driving, In-Car Shopping, Shared Mobility
The transition to SDVs is fundamental to autonomous driving, given that autonomous driving software needs continuous updates. Autonomous vehicles continue to be a major topic at CES 2024. What’s different from the past is that there is now a much wider array of use cases for autonomous mobility, from last-mile delivery vehicles to remote-driving tractors.
Other trends that accompany the SDV evolution include the growing number of in-vehicle infotainment features such as online shopping and media consumption, as well as the emergence of purpose-built vehicles made for specific use cases.

Ultimately, SDVs are creating a new ecosystem that is attracting all types of technological innovations and opportunities, an ecosystem that is more scalable and adaptable than smartphones. Therefore, SDV-related technologies are expected to dominate the tech industry for many years to come.